Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Exercises:
Understanding the Differences for Optimal Fitness
In the world of fitness, two essential categories often guide our workouts: aerobic and anaerobic exercises. Understanding these types of exercises helps us design a balanced program that targets different goals, whether building endurance or strength.

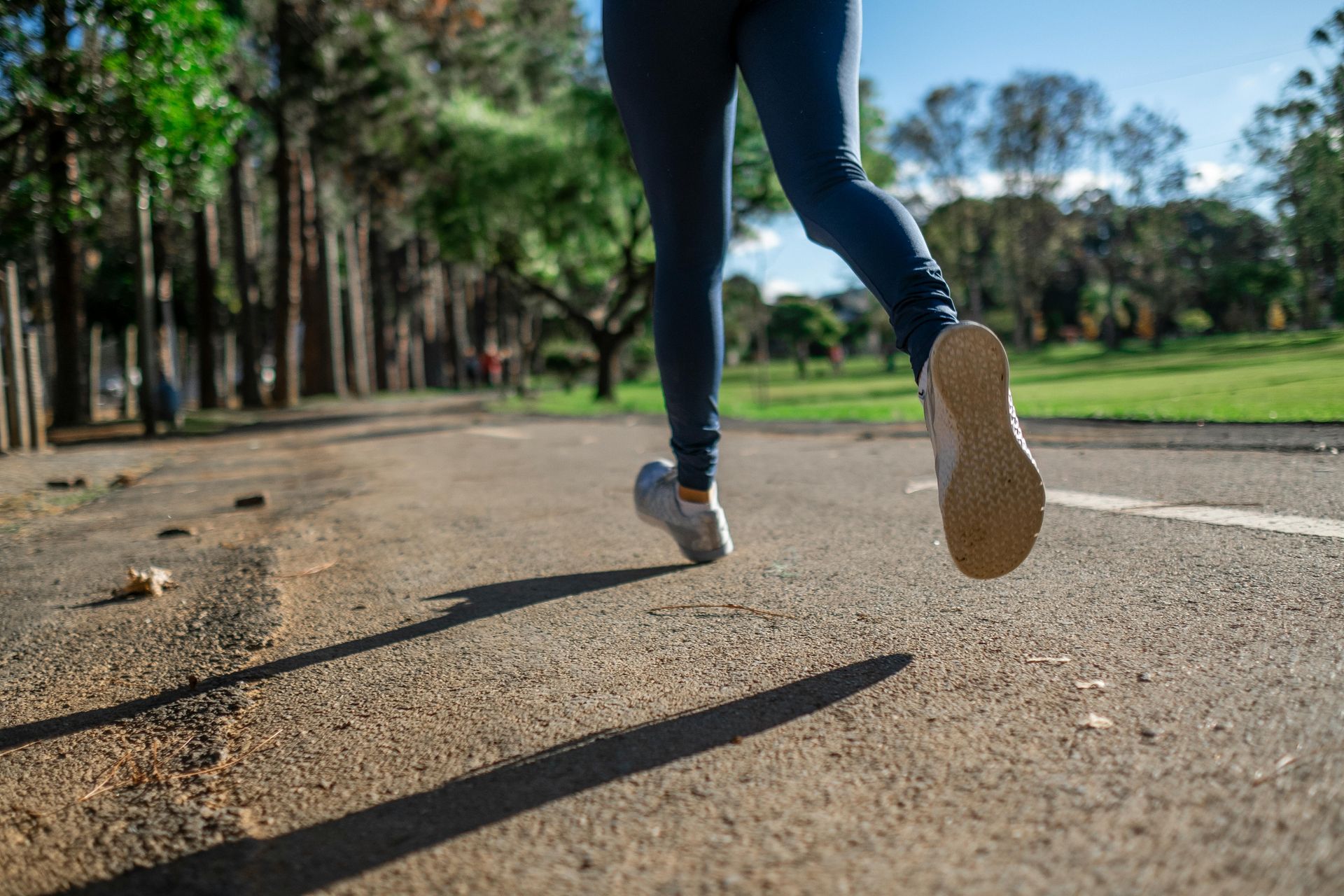
What is Aerobic Exercise?
Aerobic exercise, also known as "cardio," refers to activities that are performed at a moderate intensity over a longer period, like running, cycling, or swimming. It primarily uses oxygen to generate energy, fueling the body for sustained activity. Aerobic workouts are excellent for improving cardiovascular health, lung capacity, and overall stamina. They also aid in weight management by burning fat efficiently and enhancing your body’s endurance.
Key Benefits of Aerobic Exercise:
- Boosts cardiovascular health
- Promotes efficient oxygen usage
- Improves endurance and stamina
- Enhances mood through endorphin release
- Aids in fat loss and weight control
Aerobic workouts are typically steady-state, meaning you perform them at a consistent intensity for extended periods. This could be a 30-minute jog or a long-distance swim. The primary goal is to keep your heart rate elevated but at a sustainable level.
Optimize Your Cardio Routine: Sign up for one of our endurance-focused workouts to boost your heart health and stamina today. Click HERE to schedule a 7-Day Unlimited Pass.

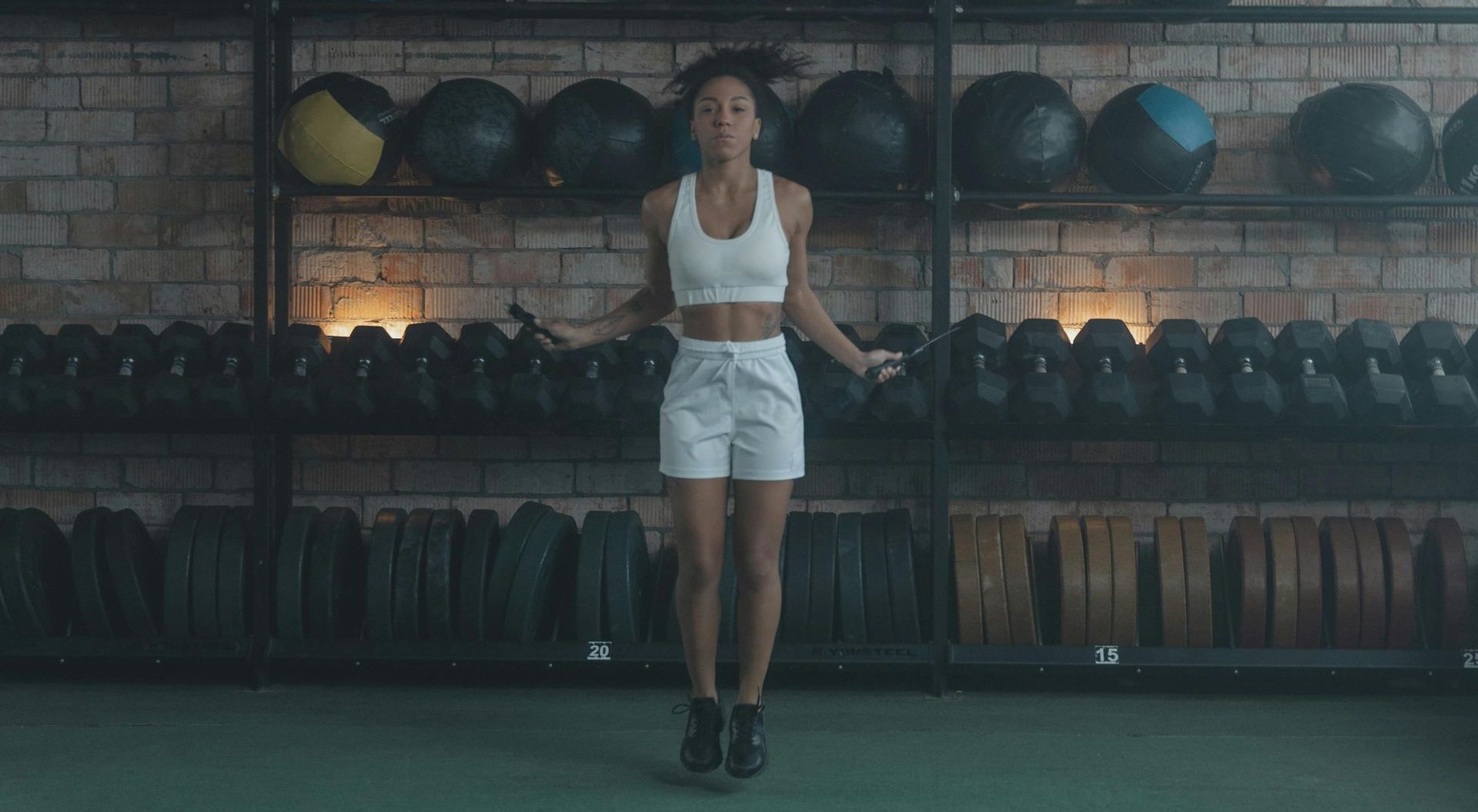
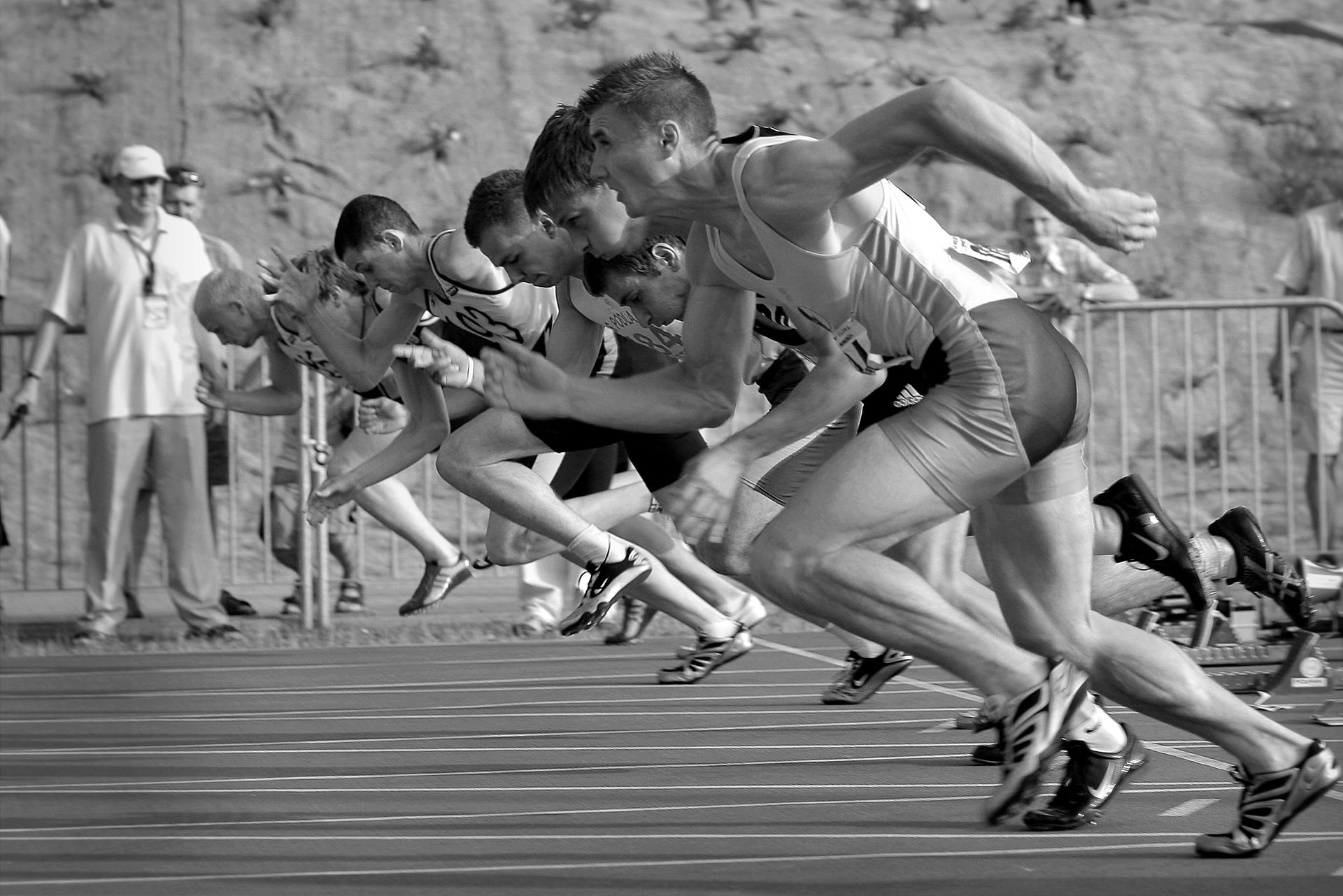
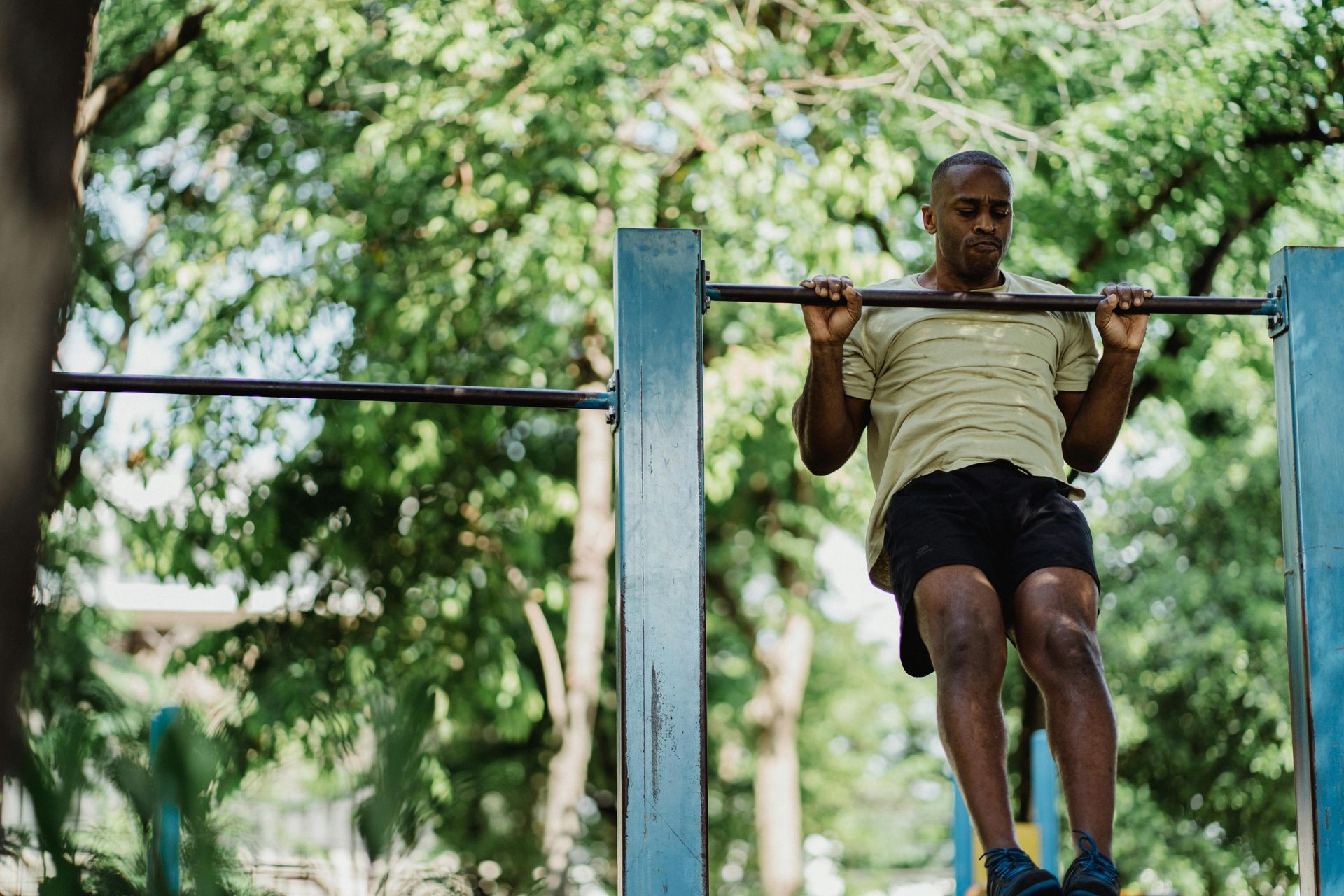
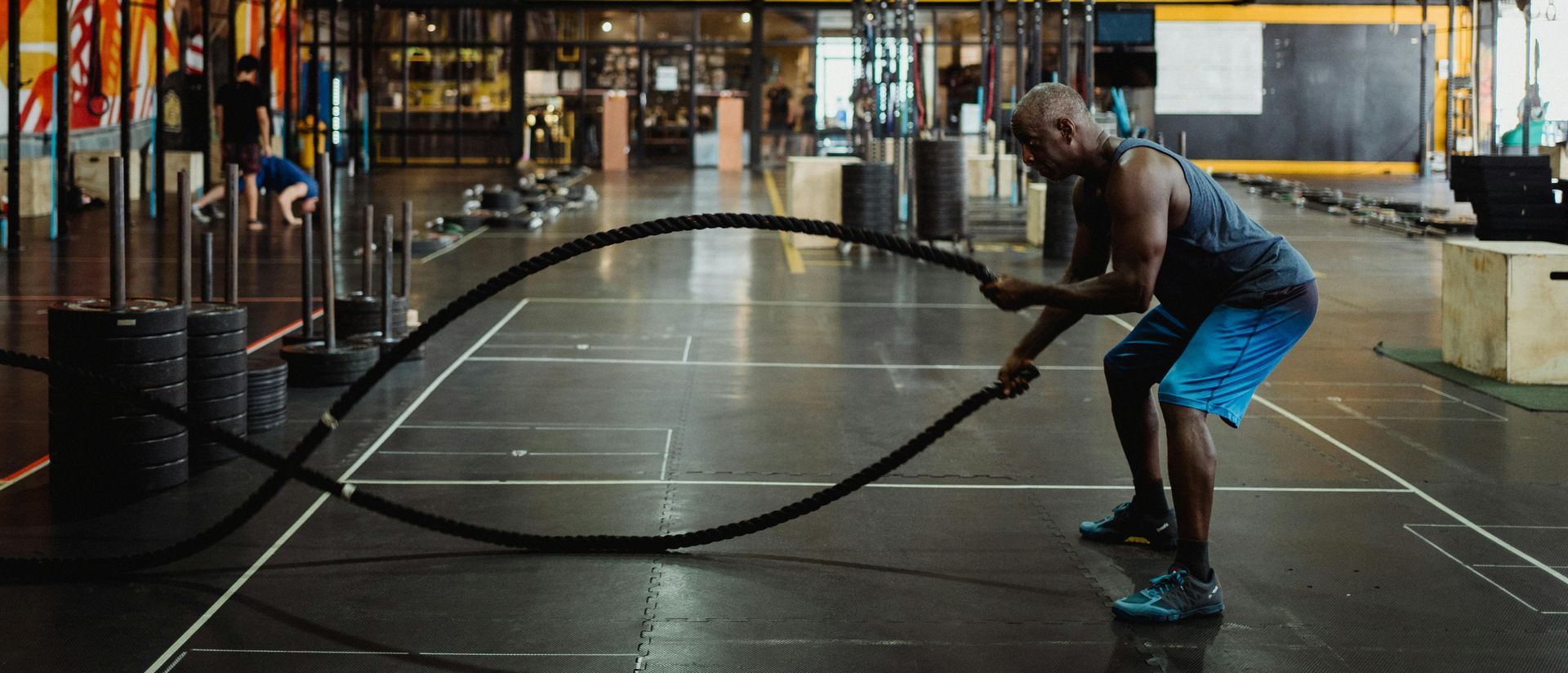
What is Anaerobic Exercise?
Anaerobic exercise involves short bursts of high-intensity activity that don’t rely on oxygen for energy. Instead, the body taps into stored glucose (glycogen) in the muscles to fuel these short efforts. Examples of anaerobic exercises include sprinting, heavy weightlifting, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). These exercises are more explosive, focusing on power, strength, and speed rather than endurance.
Key Benefits of Anaerobic Exercise:
- Builds muscle strength and power
- Increases metabolism and calorie burn post-exercise
- Enhances muscle endurance in short, intense efforts
- Helps develop fast-twitch muscle fibers
Because anaerobic exercises are so intense, they often last only a few seconds to a couple of minutes, with recovery periods in between. These exercises push your muscles to their maximum potential, resulting in improved strength, muscle mass, and a boosted metabolic rate.
Not sure where to start? Book a Free Fitness Consultation: Learn how to combine aerobic and anaerobic exercises for your personalized fitness goals.
Click HERE to schedule a session with one of our coaches.
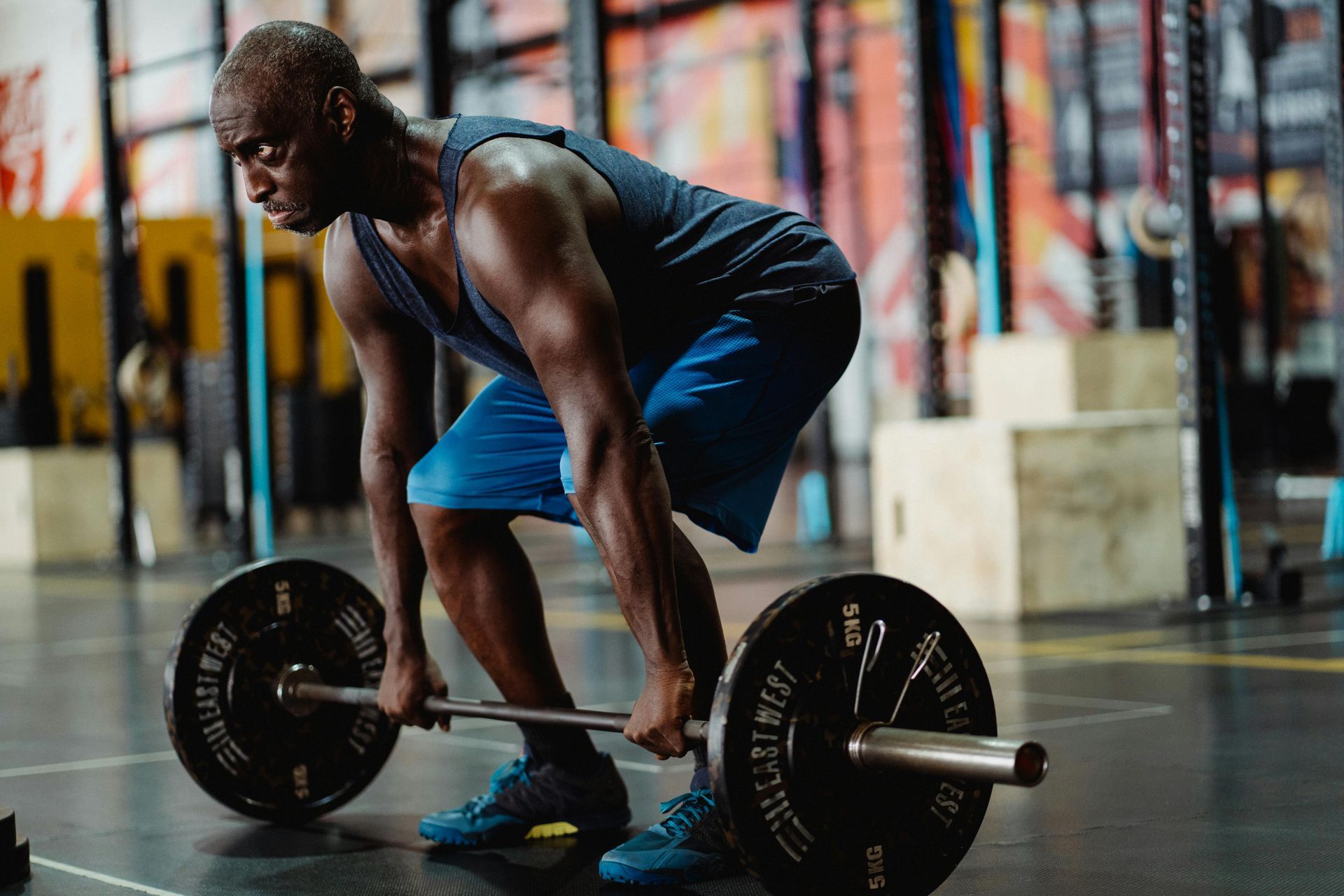

Key Differences:
While both aerobic and anaerobic exercises are beneficial, they serve different purposes. Aerobic exercises are endurance-based, improving heart health and stamina over time. On the other hand, anaerobic exercises build muscle strength, speed, and power in short bursts.
Energy Use:
- Aerobic: Relies on oxygen for energy, using fat as a fuel source.
- Anaerobic: Uses stored muscle glycogen without oxygen, resulting in lactic acid build-up (the burning sensation during intense effort).
Duration:
- Aerobic: Performed at a moderate intensity for 30 minutes or longer.
- Anaerobic: High-intensity activity performed for shorter intervals (seconds to a couple of minutes).
Incorporating Both for a Balanced Fitness Plan
Incorporating both aerobic and anaerobic exercises into your routine can help you achieve a well-rounded fitness level. Aerobic exercises help with fat loss, heart health, and endurance, while anaerobic exercises improve strength, power, and muscle tone. Together, they boost overall athletic performance and help prevent plateaus in your training.
How to Combine Aerobic and Anaerobic Workouts:
- Aerobic Focus: If you're training for endurance, include activities like jogging, cycling, or swimming several times a week. These will improve your heart and lung capacity.
- Anaerobic Focus: To build muscle and strength, add in HIIT workouts, sprinting, or weightlifting sessions a couple of times per week.
- Hybrid Training: Incorporate interval training, which combines the best of both worlds by alternating between high-intensity anaerobic bursts and moderate-intensity aerobic recovery periods.
Try Our HIIT Classes: Experience the benefits of anaerobic training by joining our next HIIT session. Improve strength and burn more calories in less time!
Click HERE to book a single class drop-in.
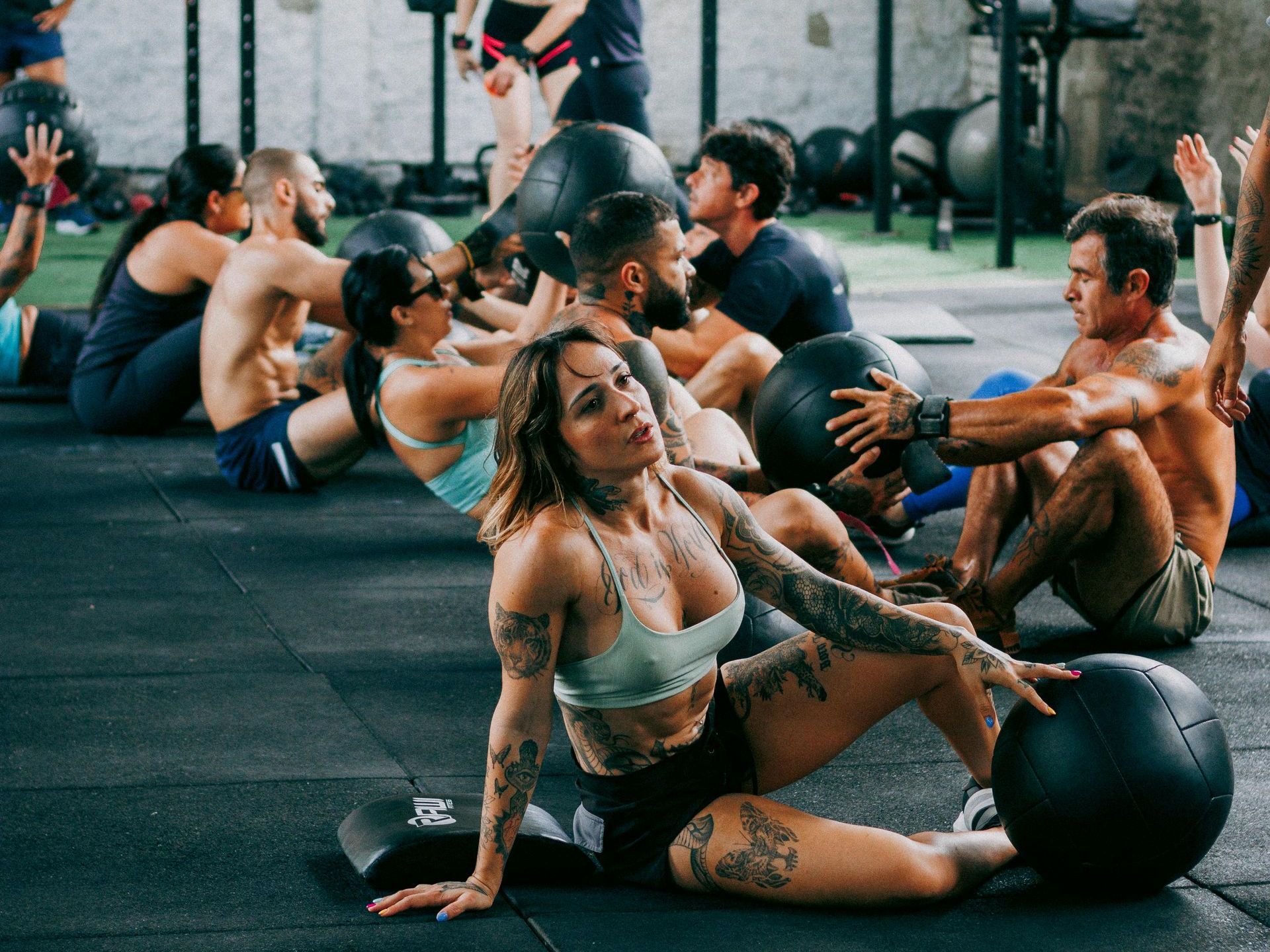

Conclusion
A well-rounded fitness routine should include both aerobic and anaerobic exercises to maximize your physical capabilities. Whether you’re aiming to run long distances, lift heavier weights, or simply stay healthy, understanding the differences between these exercise types will help you make informed decisions and get the most out of your workouts.